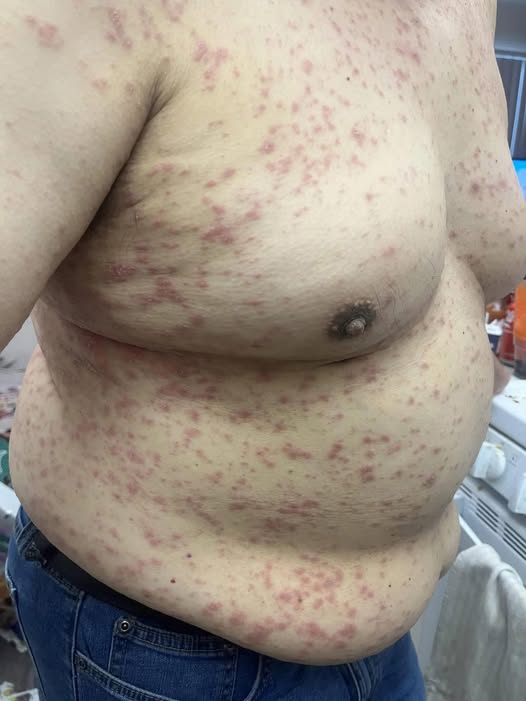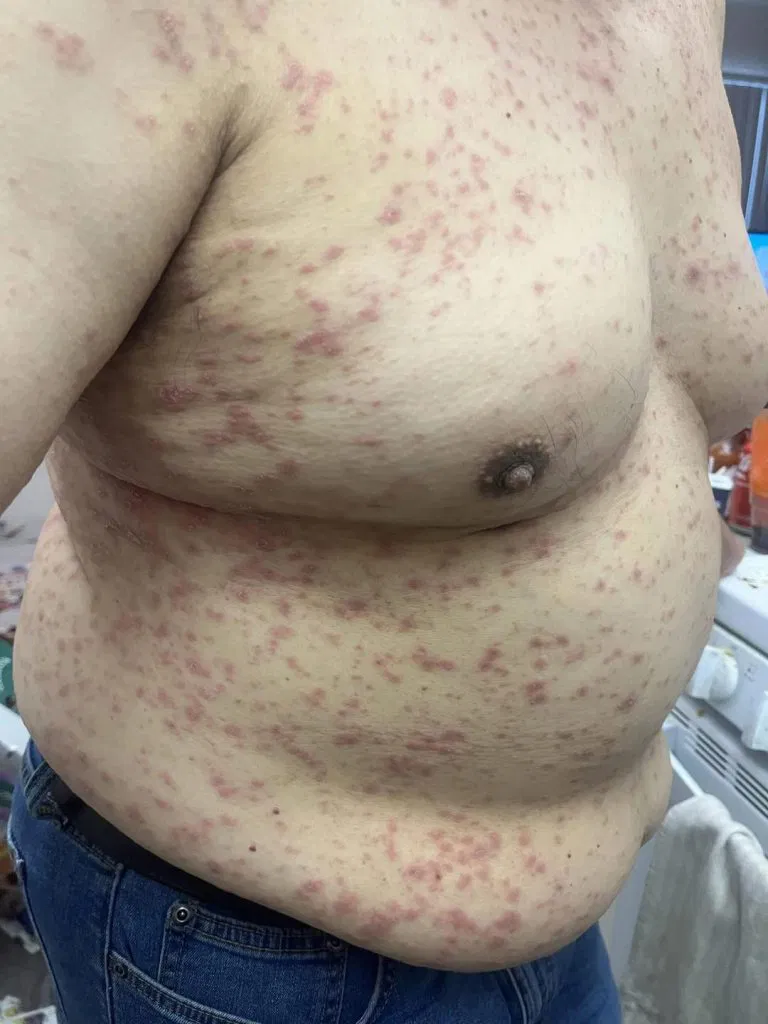
Feeling itchy on different parts of your body can be incredibly uncomfortable—and sometimes worrying. Itching (also called pruritus) can happen with or without a visible rash, appear suddenly or last for weeks, and range from mildly annoying to intense and disruptive. While itching is often harmless, in some cases it may point to an underlying issue that needs attention.
Below are the most common reasons your body may feel itchy.
1. Dry Skin (Xerosis)
Dry skin is the number one cause of generalized body itching, especially in colder weather or as we age. When the skin lacks moisture, its protective barrier weakens, leading to tightness, flaking, and itchiness.
Common triggers include:
- Hot showers
- Low humidity
- Harsh soaps
- Aging skin
Moisturizing regularly can dramatically reduce itching caused by dryness.
2. Allergic Reactions
Your skin may itch due to an allergic response to:
- Soaps, detergents, or fabric softeners
- Skincare or fragrance products
- Certain foods or medications
Allergic itching is often accompanied by redness, hives, or swelling, but mild reactions may cause itchiness alone.
3. Insect Bites and Parasites
Mosquitoes, bed bugs, mites, lice, and fleas commonly cause itchy skin. These bites usually appear as small red bumps and tend to itch more at night.
Persistent or spreading itch may indicate an infestation that needs treatment.
4. Skin Conditions
Several skin disorders cause ongoing itchiness, including:
- Eczema (atopic dermatitis)
- Psoriasis
- Contact dermatitis
- Hives (urticaria)
These conditions often involve visible rashes, scaling, or thickened skin.
5. Fungal or Bacterial Infections
Fungal infections such as ringworm or yeast thrive in warm, moist areas of the body and cause intense itching. Bacterial infections may also irritate the skin and lead to discomfort.
Common areas include the feet, groin, underarms, and skin folds.
6. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations—especially during pregnancy, menopause, or thyroid disorders—can affect skin moisture and sensitivity, leading to itching without an obvious rash.
7. Internal Health Conditions
Sometimes itching starts inside the body, not on the skin itself. Chronic or unexplained itching may be linked to:
- Liver disease
- Kidney disease
- Diabetes
- Iron deficiency
- Thyroid disorders
In these cases, itching often occurs without visible skin changes.
8. Stress and Anxiety
Emotional stress can trigger or worsen itching by affecting nerve signals and inflammation. Stress-related itching often feels worse at night and may not show obvious skin symptoms.
9. Medication Side Effects
Certain medications, including antibiotics, pain relievers, blood pressure drugs, and opioids, can cause itching as a side effect—even without a rash.
10. Nerve-Related Itching
Nerve damage or irritation from conditions such as shingles, multiple sclerosis, or spinal issues can cause localized or generalized itching without visible skin changes.
How to Relieve Body Itching at Home
- Use gentle, fragrance-free soaps
- Apply moisturizer immediately after bathing
- Avoid hot showers
- Wear loose, breathable clothing
- Use a humidifier in dry environments
- Try cold compresses for temporary relief
When to See a Doctor
You should seek medical advice if:
- Itching lasts longer than 2–3 weeks
- Itching is severe or affects sleep
- There’s no visible cause
- You experience weight loss, fatigue, or night sweats
- Skin becomes infected from scratching
Final Thoughts
Body itching is common and often caused by dry skin, allergies, or irritation. However, persistent or unexplained itch can be a signal that your body needs attention. Listening to your symptoms—and acting early—can help prevent discomfort and uncover underlying health issues.
If itching continues despite home care, a healthcare professional can help identify the cause and recommend appropriate treatment.